Planning
Describe your solo phase task
My task is to read and understand the lecture material and three articles about SRL and make ICE notes. More specifically, define three main concepts from each paper and describe 2 ideas that arose while studying this material and make notes ICE notes for them.
What topics and concepts are related to your task?
Self-regulated learning and its relationship with motivation and emotional regulation.
Set a goal for this work period
Improving my understanding of the topic and completing the assignment on time.
How confident are you that you will achieve your goal?
I might not complete my goal completely. I have been sick and wasn’t able to do the assignment on the weekend like I had planned. I might work on this more later because I had to rush this on Monday night, still feeling a little sick with mild fever.
Read articles and make ICE notes and concept definitions
Three important concepts from each article
Zimmerman, B. J. (2011). Motivational sources and outcomes of self-regulated learning and performance. In B. J. Zimmerman, & D. H. Schunk (Eds.), Handbook of self-regulation of learning and performance (pp. 49–64). New York: Routledge
1. Students may not use a strategy, which has been proven effective, because they do not enjoy using it (deficiency in self-satisfaction/affect) or do not feel the gains are worth the effort (lack of outcome expectancies).
2. Role of motivation in students’ self-regulation of learning:
High motivation can increase students’ attention
Students committed to a subject are more likely to choose to practice it on their free time (choice of task)
High motivation can increase a students effort to learn a difficult task
Highly motivated students can also be more persistent with time consuming tasks
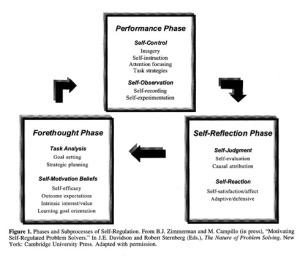
Phases and subprocesses of self-regulation. Motivational feelings/beliefs are closely intertwined with metacognitive processes within and across phases of self-regulation.
Järvenoja, H., & Järvelä, S. (2009). Emotion control in collaborative learning situations – do students regulate emotions evoked from social challenges? British Journal of Educational Psychology, 79, 463-481.
1. Teamwork was the most frequently reported challenge type
2. Self-regulation and shared-regulation were used more than other-regulation
3. There was a shift from more personal priorities challenges to collaboration-type challenges when the tasks became less structured
Wolters, C. A. (2003). Regulation of Motivation: Evaluating an Underemphasized Aspect of Self-Regulated Learning. Educational Psychologist, 38 (4), pp. 189-205.
1. Regulation of motivation can be viewed as interdependent but conceptually disticnt from other processes related to self-regulated learning including motivation, metacognition and volition.
2. Students can use a variety of disticnt strategies to regulate their motivation.
3. There is some empirical evidence linking students’ use of these strategies to important motivational, cognitive, and achievement outcomes.
Reflection
Recall your Solo phase planning. How well did you succeed? Why?
I succeeded OK
Describe one challenge that you had during your task performance.
Getting sick
What did you do to help yourself when facing a challenge?
What could you do differently next time?
Start earlier